

#Windows checksum command install
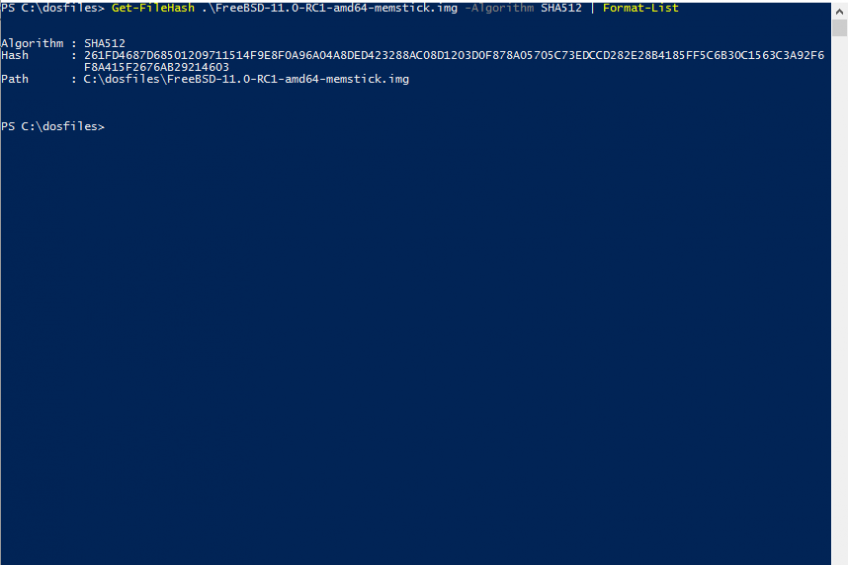
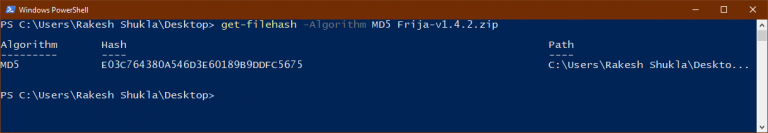
On systems that run older operating systems than Windows 8: Install a certain Windows Patch, which delivers the functionality. see of you have a different tool that can calculate SHA-256 checksums on your machine and use it instead. (Sometimes colons or spaces are used to group the checksum.) Make sure to compare it to the checksum with the right algorithm (SHA-256). It has to match for all hexadecimal digits. Once you have entered the command, it will return an alphanumeric string, which you can compare to the one on the Gpg4Win package integrity site. Open a command line, navigate to your Download-Folder, and use a command like the following, but adapt the filename to the version you have downloaded and you want to check:Ĭertutil -hashfile gpg4win-3.1.15.exe sha256 Once you have downloaded the file, you can verify that it matches the published checksums (that you have gotten via a trusted channel). SignTool verify /pa /v gpg4win*.exe Checksums For details see T3379.)Ī third way is to use MSDN:SignTool which is a part of the Microsoft development tools: Open open a command line, navigate to the folder and enter
(Try this if no publisher is shown by the UAC in rare cases after a download with Firefox or Iridium (Chromium). Right click on the installer -> properties -> digital signatures -> Details of signatures. :) (If you have disabled User Access Control use a different method.)Ī second way is to use the file properties in the explorer. When trying to run the installer on Windows, the User Access Control dialog will show the publisher, check that it is the one you expected it to be. Windows can check the integrity and the publisher of a signed software package. The signature informations used to code sign the packages can be found on the Gpg4Win package integrity site.
All Gpg4win installer files since April 2016 are code signed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
